At the heart of the decentralized finance ecosystem lie crypto trading nodes — vital components of blockchain networks responsible for validating transactions, maintaining a distributed ledger, and ensuring network consensus. These nodes act as communication hubs, relaying information and verifying the legitimacy of each transaction batch, known as blocks.
Crypto trading nodes are the unsung heroes of the DeFi space, enabling the peer-to-peer exchange of digital assets without the need for a centralized authority. By running a node, individuals or organizations contribute to the security and stability of the network, helping to prevent fraud and maintain the immutability of the blockchain.
The Different Types of Crypto Trading Nodes
 What are Blockchain nodes? Detailed Guide
What are Blockchain nodes? Detailed Guide
In the world of crypto trading, there are several distinct types of nodes, each with its own unique functionalities and capabilities. Understanding these variations is crucial for investors to make informed decisions about their involvement in the DeFi landscape.
Full Nodes
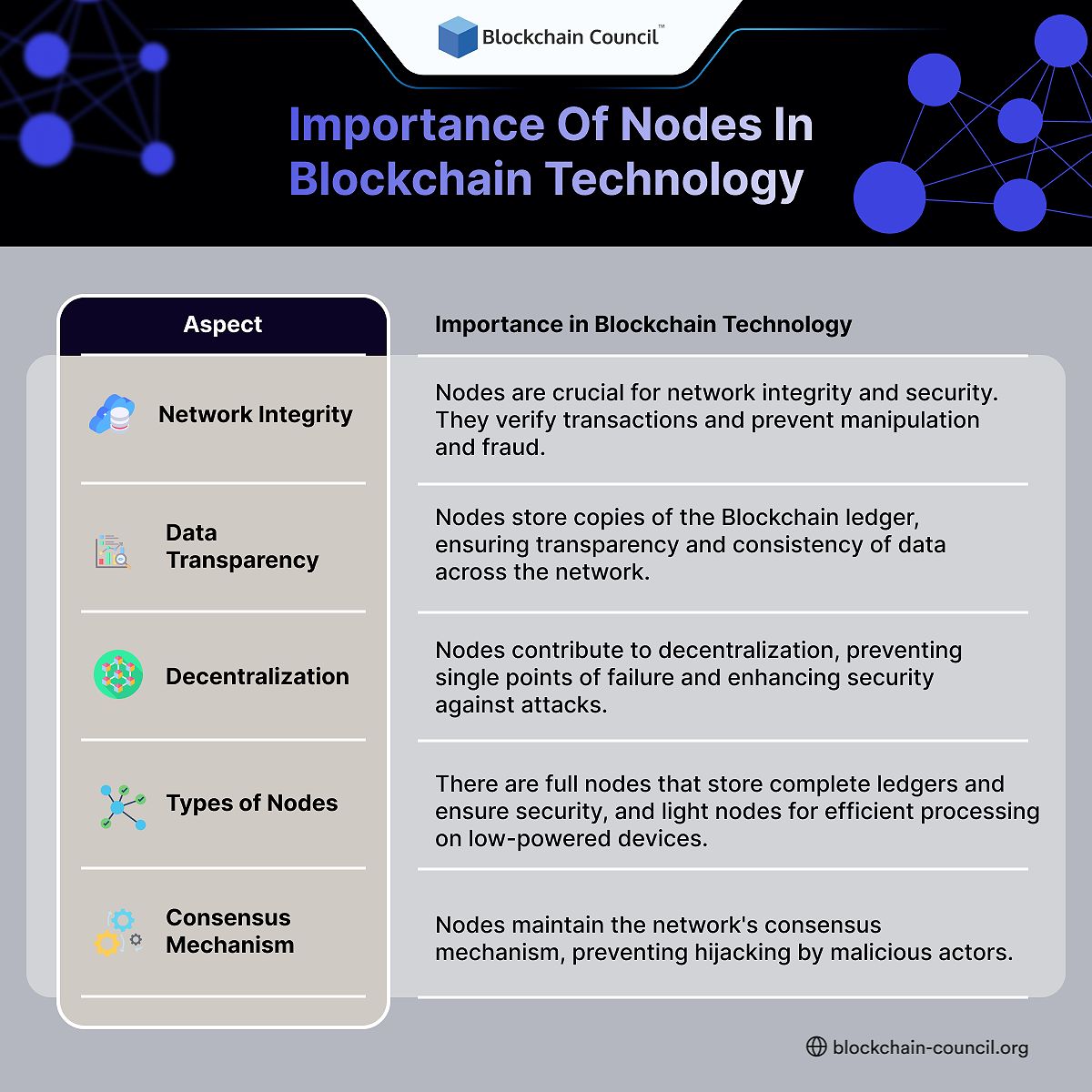 Importance of nodes in Blockchain technology
Importance of nodes in Blockchain technology
Full nodes are the most comprehensive type of crypto trading node, as they store a complete copy of the blockchain and independently validate all transactions. These nodes play a critical role in maintaining the security and stability of the network, contributing to the overall consensus and helping to prevent malicious activities.
Advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Full nodes offer the highest level of security, as they can independently verify the entire blockchain.
- Complete Data Access: By storing a complete copy of the blockchain, full nodes have access to the entire transaction history.
- Contribution to Network Stability: Full nodes are essential for maintaining the stability and reliability of the blockchain network.
Drawbacks:
- High Resource Requirements: Running a full node requires significant computing power, storage space, and a stable internet connection, which can be a barrier to entry for some users.
- Technical Complexity: Setting up and maintaining a full node can be a complex process, requiring a certain level of technical expertise.
- Potential for Downtime: Full nodes are vulnerable to power outages, hardware failures, or network disruptions, which can lead to temporary disruptions in the network.
Light Nodes
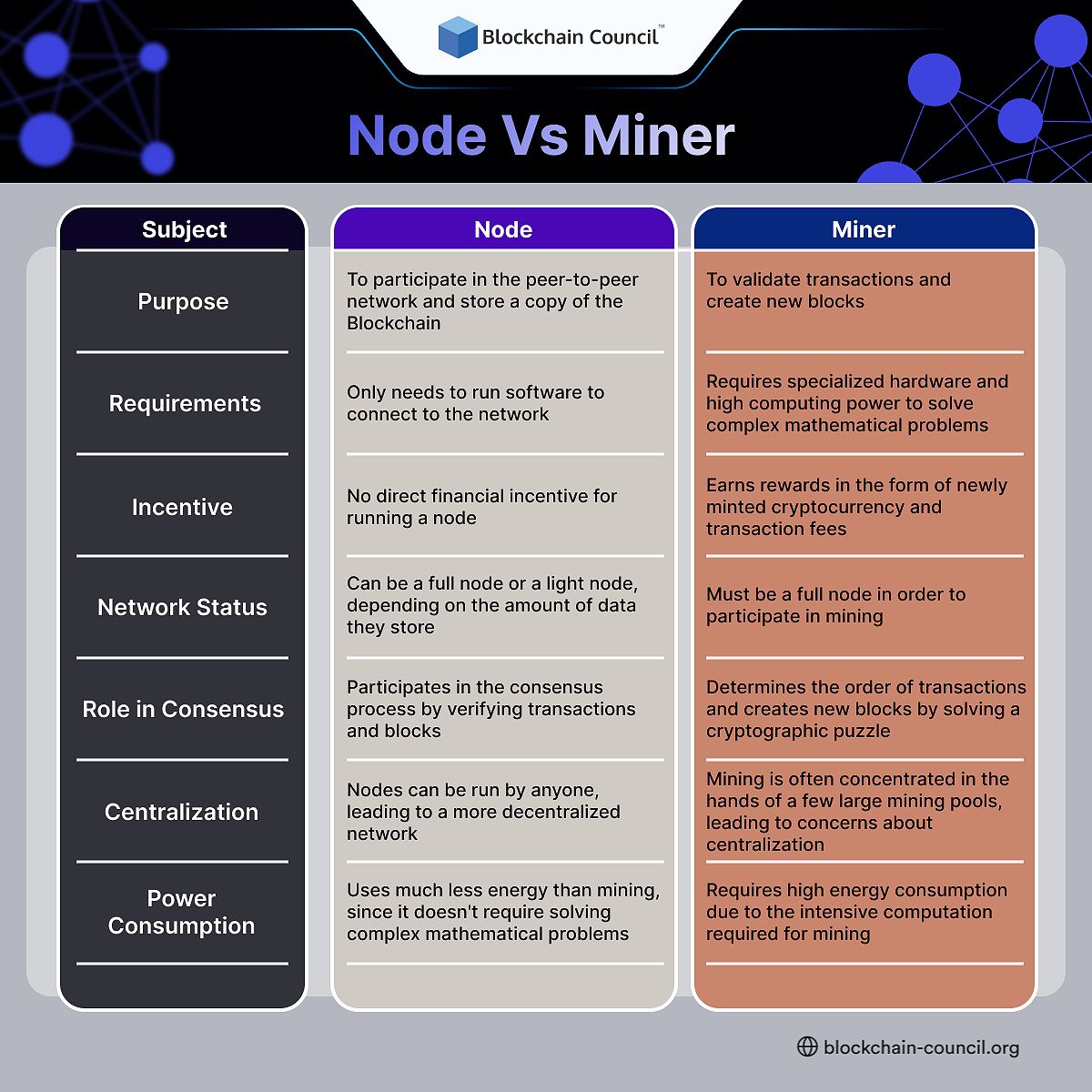 Node Vs. Miner
Node Vs. Miner
Light nodes, also known as Simplified Payment Verification (SPV) nodes, are a more lightweight alternative to full nodes. These nodes store only a portion of the blockchain, relying on full nodes to validate transactions and maintain the overall network.
Advantages:
- Lower Resource Requirements: Light nodes have lower hardware and storage requirements, making them more accessible for users with limited resources.
- Faster Operation: Light nodes can process transactions more quickly, as they don’t need to download the entire blockchain.
- Easier Setup: Setting up a light node is generally a simpler process compared to a full node.
Drawbacks:
- Reduced Security: Light nodes rely on full nodes for transaction validation, which means they have a lower level of security compared to their full node counterparts.
- Dependence on Full Nodes: Light nodes are dependent on the availability and reliability of full nodes to function correctly.
- Limited Data Access: Light nodes only have access to a portion of the blockchain, which means they have a limited view of the network’s transaction history.
Master Nodes
Master nodes are a specialized type of crypto trading node that offer additional services beyond basic transaction validation. These nodes often require a significant investment in cryptocurrency as collateral and can provide enhanced privacy features or governance rights within the network.
Advantages:
- Increased Earning Potential: Master node operators can earn rewards for their contributions to the network, such as transaction fees or block rewards.
- Governance Rights: In some blockchain networks, master nodes may have a say in the decision-making process, giving their operators a voice in the network’s future.
- Enhanced Privacy: Certain master node configurations can offer improved privacy features for users, such as anonymous transactions or obfuscation of transaction histories.
Drawbacks:
- High Entry Cost: Running a master node often requires a substantial investment in the network’s cryptocurrency, which can be a barrier to entry for some users.
- Potential for Technical Complexity: Setting up and maintaining a master node may require a higher level of technical expertise compared to other node types.
- Risk of Losing Collateral: If a master node operator violates the network’s rules or fails to maintain their node, they may risk losing the collateral they have staked.
Mining Nodes
 Binary code and blockchain nodes surrounding a digital outline of the continents.
Binary code and blockchain nodes surrounding a digital outline of the continents.
Mining nodes are responsible for verifying transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain in proof-of-work (PoW) networks, such as Bitcoin. These nodes use specialized hardware and software to solve complex mathematical problems, competing to be the first to validate a block and earn the associated cryptocurrency rewards.
Advantages:
- Potential for Earning Rewards: Mining node operators can earn cryptocurrency rewards for successfully validating and adding new blocks to the blockchain.
- Contribution to Network Security: By validating transactions and adding new blocks, mining nodes help to maintain the overall security and integrity of the blockchain network.
Drawbacks:
- High Energy Consumption: The computational power required for mining can result in significant energy consumption, which can be a concern for both environmental and cost perspectives.
- Expensive Hardware: Running a mining node often requires specialized and expensive hardware, such as application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) or graphics processing units (GPUs).
- Potential for Obsolescence: As blockchain networks evolve and new mining hardware is developed, existing mining equipment may become obsolete, leading to decreased profitability and the need for regular hardware upgrades.
Staking Nodes
Staking nodes are used in proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain networks, where participants lock up (or “stake”) their cryptocurrency as collateral to validate transactions and earn rewards. These nodes help to secure the network and maintain consensus without the high energy consumption associated with mining.
Advantages:
- Lower Energy Consumption: Staking nodes do not require the intensive computational power needed for mining, making them a more energy-efficient option.
- Potential for Earning Rewards: Staking node operators can earn rewards for their contributions to the network, such as transaction fees or newly minted cryptocurrency.
- Contribution to Network Security: By staking their cryptocurrency, node operators have a vested interest in maintaining the integrity of the network, helping to enhance its overall security.
Drawbacks:
- Requires Locking Up Cryptocurrency: To operate a staking node, users must lock up a portion of their cryptocurrency as collateral, which may limit their ability to trade or use those funds in the short term.
- Potential for Loss of Collateral: If a staking node operator violates the network’s rules or fails to maintain their node, they may risk losing their staked cryptocurrency.
- Technical Knowledge Required: Setting up and maintaining a staking node may require a certain level of technical expertise, which can be a barrier to entry for some users.
The Inner Workings of Crypto Trading Nodes
Crypto trading nodes play a pivotal role in the overall functionality and security of decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and the broader DeFi ecosystem. By understanding the key processes involved in node operation, investors can gain a deeper appreciation for the significance of these unsung heroes.
Transaction Validation
When a user initiates a transaction, it is broadcast to the network and received by a node. The node then independently verifies the authenticity of the transaction, checking for valid signatures, sufficient funds, and adherence to the blockchain’s rules. This process helps to prevent fraud, double-spending, and other malicious activities, ensuring the integrity of the network.
Network Consensus
Crypto trading nodes work together to reach a consensus on the order of transactions and the current state of the blockchain. This is achieved through various consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS), which ensure that all nodes in the network agree on the validity of the transaction history.
Data Storage and Synchronization
Nodes maintain a copy of the blockchain, which they regularly synchronize with other nodes in the network. This distributed data storage model helps to preserve the immutability of the blockchain, as any attempt to alter the transaction history would require the agreement of a majority of the nodes.
DEX Operation
Crypto trading nodes are essential for the smooth operation of decentralized exchanges. By enabling peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a centralized intermediary, nodes contribute to the speed, efficiency, and security of DEX platforms, empowering users to take control of their own financial transactions.
The Benefits of Running a Crypto Trading Node
Running a crypto trading node can offer a range of benefits, from earning rewards to contributing to the overall security and decentralization of the DeFi ecosystem.
Earning Rewards
Depending on the blockchain network and the type of node being operated, node owners may be eligible to earn rewards, such as block rewards, transaction fees, or staking rewards. These incentives can provide a passive income stream for dedicated node operators.
Contributing to Network Security
By running a node, individuals and organizations can play a vital role in maintaining the security and integrity of the blockchain network. Nodes help to prevent malicious activities, ensure the immutability of the transaction history, and promote a more decentralized and equitable ecosystem.
Enhanced Control Over Transactions
Operating a node allows users to have more control over their own transactions, as they can independently validate them and choose which nodes to interact with. This level of autonomy is a core tenet of the decentralized finance movement.
Supporting Decentralization
Participating in the operation of a crypto trading node contributes to the overall decentralization of the DeFi ecosystem, reducing the reliance on centralized entities and promoting a more transparent and equitable financial system.
FAQ
Q: What are the minimum requirements for running a crypto trading node? A: The minimum requirements for running a crypto trading node can vary depending on the specific blockchain network, but generally, you’ll need a computer or server with sufficient processing power, storage space, and a stable internet connection. The exact specifications may also depend on whether you’re running a full node or a more lightweight version.
Q: How do I choose the right blockchain network to run a node on? A: When selecting a blockchain network to run a node on, consider factors such as the platform’s popularity, security, reward structure, and technical complexity. Research the network’s consensus mechanism, community support, and potential for growth, as these elements can impact the benefits and challenges of running a node.
Q: Are there any risks associated with running a crypto trading node? A: Yes, there are some risks involved in running a crypto trading node, including security threats (such as malware attacks, DDoS attacks, and Sybil attacks), technical complexity, and resource requirements. It’s essential to take appropriate measures to secure your node, maintain it properly, and be prepared to troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving world of decentralized finance, crypto trading nodes have emerged as the unsung heroes, playing a pivotal role in validating transactions, maintaining network consensus, and ensuring the overall security and integrity of blockchain networks. By understanding the different types of nodes, their functionalities, and the processes involved in their operation, investors can make more informed decisions about their involvement in the DeFi space.
As the cryptocurrency market continues to grow and mature, the importance of crypto trading nodes will only increase, as they remain the backbone of the decentralized infrastructure that enables peer-to-peer transactions and promotes financial inclusivity. By considering the potential benefits and risks associated with running a node, you can explore the opportunities to contribute to the DeFi revolution and potentially earn rewards for your efforts.
Whether you’re a seasoned investor or new to the world of decentralized finance, delving into the world of crypto trading nodes can provide valuable insights and empower you to navigate the ever-evolving cryptocurrency landscape with confidence and success.

