Cryptocurrency trading has become increasingly popular, making it essential to understand the tax implications of your activities. This guide provides comprehensive information on taxes on crypto trading, whether you are a seasoned investor or just starting your journey. We will cover the tax considerations surrounding your crypto trading endeavors, equipping you with the knowledge and strategies to manage your tax obligations effectively.
Classifying Crypto as Property: The IRS Perspective
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has unequivocally classified cryptocurrencies as property, similar to stocks, bonds, or real estate. This classification has significant implications for how your crypto trading activities are taxed.
Unlike traditional currencies, which are not subject to capital gains taxes, any time you buy, sell, or exchange cryptocurrencies, you’re susceptible to potential tax consequences. Even if you don’t convert your crypto back to fiat (traditional) currency, the IRS views these transactions as a disposal of the original asset, triggering capital gains or losses.
Identifying Taxable Events in Crypto Trading
Understanding the various scenarios that constitute taxable events is essential for accurate tax reporting. Let’s explore the most common situations:
- Selling Crypto for Fiat Currency: When you convert your cryptocurrency holdings into traditional fiat currencies, such as US dollars, you’ll need to report any capital gains or losses on your tax return. The amount of tax you owe will depend on whether the gains are classified as short-term or long-term.

- Trading Crypto for Other Crypto: Even if you don’t cash out your crypto to fiat, exchanging one cryptocurrency for another is still considered a taxable event by the IRS. You’ll need to calculate the capital gains or losses based on the fair market value of the new cryptocurrency you received.
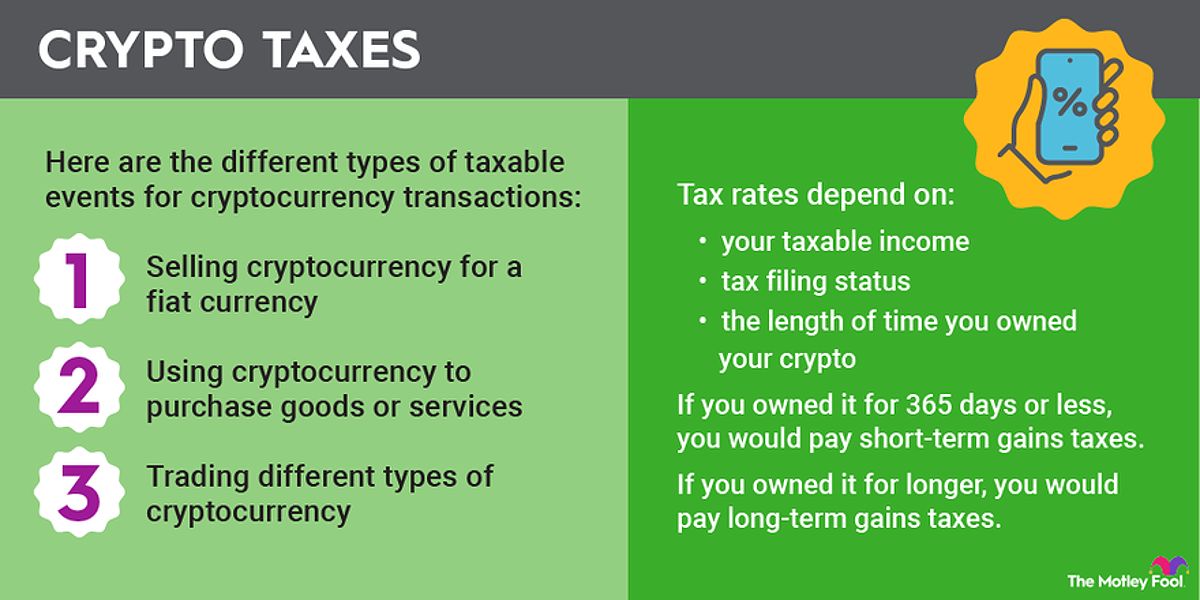
- Using Crypto for Purchases: Utilizing your cryptocurrency to purchase goods or services is also treated as a taxable transaction. The fair market value of the crypto at the time of the purchase will be your cost basis, and any gains or losses must be reported accordingly.
Maintaining meticulous records of all your crypto trading activities is crucial to ensure accurate tax reporting. This includes details such as the purchase date, sale date, cost basis, and proceeds for each transaction.
Understanding Taxes on Crypto Trading
The tax rates applied to your crypto trading gains or losses depend on the length of time you held the assets before selling or exchanging them.
- Short-Term Capital Gains: If you held the cryptocurrency for one year or less before selling or exchanging it, any profits will be taxed as short-term capital gains. These gains are subject to your ordinary income tax rates, which can range from 10% to 37% in the 2024 tax year, depending on your taxable income and filing status.
- Long-Term Capital Gains: If you held the cryptocurrency for more than one year before selling or exchanging it, any profits will be taxed at the more favorable long-term capital gains rates. For the 2024 tax year, the long-term capital gains tax rates are 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your taxable income and filing status.
It’s important to note that higher-income taxpayers may also be subject to the 3.8% Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) on their crypto trading gains.
Strategies to Minimize Your Crypto Trading Tax Burden
While the IRS requires you to pay taxes on your crypto trading activities, there are several strategies you can employ to potentially reduce your tax liability:
- Tax Loss Harvesting: If you have realized losses on some of your crypto investments, you can use those losses to offset your capital gains from other profitable trades. This process, known as tax loss harvesting, can help lower your overall tax burden.
- Long-Term Holding: By holding your cryptocurrency for more than a year before selling, you can benefit from the lower long-term capital gains tax rates. This can result in significant tax savings compared to short-term gains.
- Crypto IRA: Investing in a crypto-specific individual retirement account (IRA) can provide tax-deferred or tax-free growth, depending on the type of IRA you choose. This can be a valuable strategy for your long-term crypto investment goals.
Reporting Crypto Trading Taxes
When it comes to filing your taxes, you’ll need to report your crypto trading activities on several forms:
- Form 8949: This form is used to report your capital gains and losses from the sale or exchange of crypto assets.
- Schedule D: This form summarizes your total capital gains and losses, including those from crypto trading.
- Form 1040: Your crypto trading gains or losses will ultimately be reported on your individual income tax return.
Additionally, some cryptocurrency exchanges may provide you with a Form 1099-B, which reports your proceeds from broker and barter exchange transactions. Maintaining accurate records of all your crypto transactions is crucial, even if you don’t receive a 1099-B.
Stay Informed and Seek Professional Guidance
Navigating the complexities of crypto taxes requires staying up-to-date with the latest IRS guidelines and regulations. As the crypto landscape continues to evolve, it’s essential to consult with a qualified tax professional who can provide personalized advice and guidance.
By understanding the tax implications of your crypto trading activities, employing strategic tax minimization techniques, and maintaining meticulous records, you can confidently manage your tax obligations and focus on growing your crypto investments.
Remember, the key to successfully navigating the crypto tax maze is to remain informed, proactive, and diligent in your record-keeping. With the right approach, you can maximize your crypto returns while ensuring compliance with the IRS.
FQAs
Q1: What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains in crypto trading? The key distinction lies in the holding period. Short-term capital gains apply to crypto assets held for one year or less, and they are taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. Long-term capital gains apply to crypto assets held for more than one year and are generally taxed at lower, preferential rates.
Q2: How do I calculate my cost basis for cryptocurrency? Your cost basis is the original amount you paid to acquire the cryptocurrency. This includes the purchase price and any fees or commissions paid. If you received the crypto through mining, staking, or as a gift, the cost basis is the fair market value at the time of receipt.
Q3: Do I need to report all crypto transactions on my tax return? Yes, you are required to report all taxable crypto transactions, including sales, exchanges, and using crypto for purchases. Even if the transaction resulted in a loss, you must still report it on your tax return.
Q4: Can I deduct losses from crypto trading on my taxes? Yes, you can deduct crypto trading losses, but there are some limitations. You can use these losses to offset your capital gains from other investments, as well as up to $3,000 of your ordinary income per year. Any unused losses can be carried forward to future tax years.

